What Are Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) and How Do They Work?
A Beginner's Guide to Web5 Technology
Introduction
Imagine stepping into a world where the internet isn't housed in data centers owned by a few tech giants but is instead a sprawling, vibrant tapestry woven by countless individual threads, each thread representing a user like you and me. This is the world of Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) - a cornerstone of the revolutionary Web5 infrastructure.
At the heart of Web5's infrastructure, DWNs signify a transformative shift from the traditional centralized web hosting model towards a more distributed, decentralized, and user-centric framework as opposed to the current web structures, dominated by centralized servers, thereby posing significant challenges in terms of privacy, security, and data sovereignty.
This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of what DWNs are, their operational mechanics, and the role they play in heralding a new era of internet technology.
Understanding Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs)
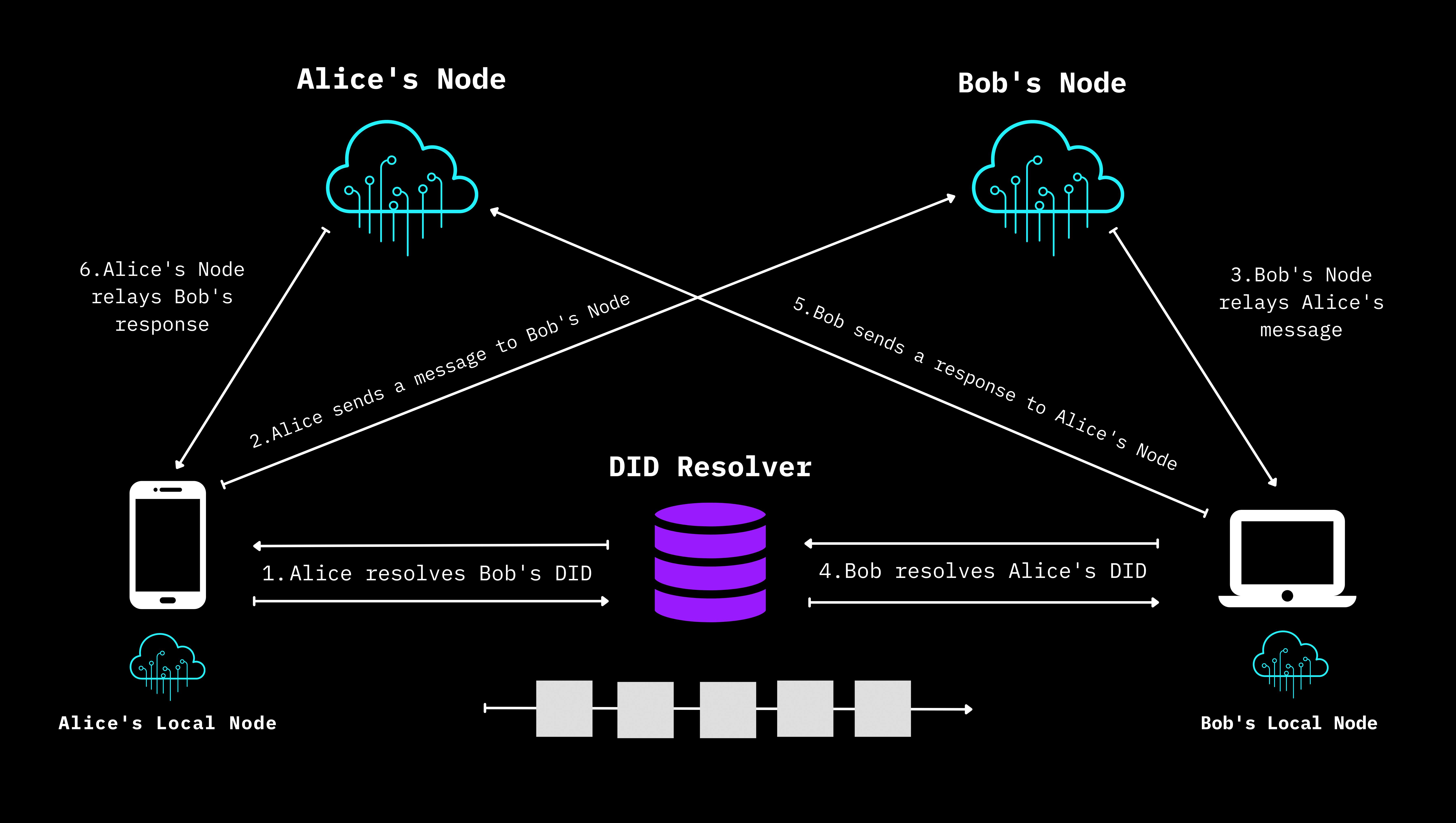
Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) represent a fundamental component in the architecture of the decentralized web, often associated with the emerging concept of Web5. Picture a vast ocean where every drop of water contributes to its vastness. Similarly, Decentralized Web Nodes are like these individual drops, each contributing to the vastness of the internet.
This innovative approach marks a significant departure from the traditional model of web servers, which are typically centralized and controlled by specific entities or organizations.
In a DWN framework, users gain more control over their personal information, reducing dependency on centralized platforms that traditionally monopolize data management. This shift is not merely technological but also philosophical, promoting a more democratized and equitable internet landscape.
How Do Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) Work?
Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) work in a series of ways which can be categorized as the following:
Distribution of Data
In the DWNs realm, data is like a story shared among friends, each holding a part of the tale. Rather than storing data in a solitary vault, it's spread across a network of nodes, each holding a piece of the overall puzzle.
This means that instead of storing data in a single location, DWNs distribute it across a network of multiple nodes. Each node in this network holds a segment of the overall data.
Peer-to-Peer Network
DWNs are structured as a community where everyone both gives and takes, creating a balanced ecosystem. That's the peer-to-peer model of DWNs, where each node plays a dual role – a giver and a receiver. This mutual exchange not only strengthens the network but also democratizes it.
In this arrangement, each node functions both as a server and a client, simultaneously contributing to and utilizing resources within the network. This means that every participant in the network shares a portion of the network's load, facilitating a more efficient and balanced distribution of resources.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Availability
DWNs ensure that each piece of data is like a well-guarded treasure, secure and authentic. No matter where the data resides, its integrity remains unblemished, maintaining the trust and reliability of the network.
This is achieved through advanced cryptographic techniques, which secure each data transaction or exchange within the network. Cryptography ensures that the data is not only secure but also consistently verifiable, regardless of the node it resides on.
Utilizing Consensus Mechanisms
DWNs employ consensus mechanisms compared to a democratic voting system, which are essential for the nodes to collectively agree on the network's state and validate transactions. Different DWNs might use various consensus protocols, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), each with its own unique characteristics and advantages.
Advantages of Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs)
Decentralized Web Nodes (DWNs) offer a multitude of advantages over traditional centralized web systems, fundamentally altering the landscape of data storage, security, and user autonomy on the internet. These benefits include:
Enhanced Security
One of the most significant benefits of DWNs is the enhanced level of security they provide. In a decentralized network, data is not stored in a single location but is distributed across multiple nodes. This distribution inherently reduces the risk of large-scale cyber-attacks and data breaches. Unlike centralized systems, where a single point of compromise can lead to widespread data loss or exposure, DWNs require attackers to breach multiple nodes simultaneously, a feat that is exponentially more difficult. This decentralized approach to data storage ensures a higher level of security and protection for sensitive information.
Data Sovereignty
DWNs empower users with greater control over their personal data, which is like having a personal vault for your digital identity, accessible only by you. Users are not just passive participants in the digital space but active controllers of their own data. This means they have the power to decide how, where, and by whom their information is used. This level of autonomy and control contrasts the traditional models where data is often at the mercy of centralized entities.
Reduced Downtime
The decentralized nature of DWNs also contributes to reduced network downtime. In a DWN framework, the failure of one or several nodes does not cripple the entire network. Other nodes can continue to operate and maintain the network's functionality. This resilience against failures ensures consistent availability and access to data, making DWNs a reliable choice for critical applications and services.
Censorship Resistance
In a decentralized network, no single entity has complete control over the information. This makes it incredibly challenging for any individual or group to manipulate, censor, or control the flow of information. The decentralized architecture of DWNs promotes a free and open internet where information can be shared without undue influence or control by any central authority.
Conclusion
Decentralized Web Nodes are a cornerstone of the Web5 vision, offering a more secure, private, and user-controlled Internet experience. This detailed breakdown offers an insight into the operational framework of DWNs, highlighting their significance in the context of the evolving internet landscape. DWNs not only enhance the technical robustness of web infrastructure but also foster a more democratic and user-empowered digital world.
Helpful content: